Have you heard of Omega 10?
Omega 10 is a new concept of combining Omega 3 DHA with Omega 7, which provides a more complete Omega formula for cardiovascular health. While you’re probably familiar with DHA, Omega 7 is probably new to you. Omega 7 is a new Omega discovered at the Harvard School of Public Health in 2008. Emerging researches have shown promising results of Omega 7, especially for lipid metabolism.
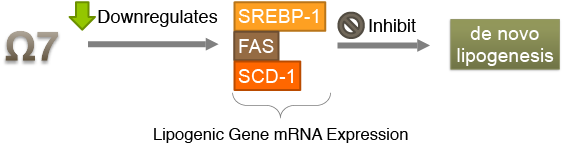
Different from DHA, Omega 7 acts as a lipid hormone signaling molecule (Lipokine). It helps signal our body to use fat for energy and decrease our appetite, improving lipid metabolism. Moreover, it also helps muscles to be more insulin sensitive and hence promoting glucose metabolism. In a study conducted by Harvard University, over 400 fatty acids were screened and it was suggested that Omega 7 could be "the only fatty acid that could substantially change serum fatty acid composition in relation to alterations in lipid metabolism in adipose tissue." (Cao et al., 2008)
Mechanism of Action of Omega 7
Researches have also shown that Omega 7 is effective in preventing cardiovascular disease and plays a key role in metabolic syndrome, which helps in:
Lowering LDL
Increasing HDL
Reducing blood sugar and serum triglyceride
Maintaining normal blood pressure
Reducing insulin resistance
Fighting chronic inflammation
Suppressing appetite to aid weight management
In a 30-day clinical study with 60 healthy participants, oral intake of 220.5mg Omega 7 per day showed a significant reduction in C-Reactive Protein (CRP) by 44%, Triglyceride (TG) by 15%, Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) by 8% and a significant increase in High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) by 5%. (Bernstein, Roizen and Martinez, 2014)
Identification of a Lipokine, a Lipid Hormone Linking Adipose Tissue to Systemic Metabolism (Bernstein, Roizen and Martinez, 2014)
Apart from Omega 7, sea buckthorn oil has additional advantageous components not found in fish or microalgae oil. Originated from the Himalayas, sea buckthorn is naturally grown with more than 190 bioactive nutrients, including 17 Vitamins, 14 minerals, and 18 amino acids. These nutrients can act as potent antioxidants and protect DHA from oxidation, which is the main cause of the unpleasant rancid smell of fish oil.
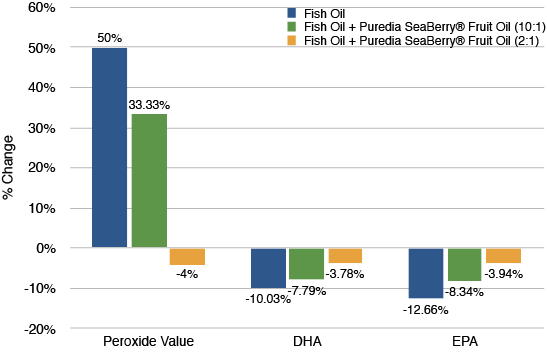
To further investigate this, our R&D team combined fish oil with sea buckthorn oil and researched on its thermal stability. The mixture was heated to 105 °C for 1 hour to speed up the oxidation process. The result showed that the mixture is 54% lower in peroxide value and loss in DHA (6.25% less) and EPA (8.72% less) is reduced, when compared with pure fish oil.
Comparison of Thermal Stability of Fish-Seabuckthorn Oil Mixture
Puredia Omega 10 Featured Product:
Oil Form
DHA (TG) ≥ 20%
Omega 7 (TG) ≥ 20%
Omega 9 ≥ 8%
Beta-carotene ≥ 400mg/100g
Vitamin E ≥ 100mg/100g
Learn More >>
Water-soluble Powder Form
DHA (TG) ≥ 5%
Omega 7 (TG) ≥ 5%
Omega 9 ≥ 2%
Beta-carotene ≥ 40mg/100g
Vitamin E ≥ 300mg/100g
Learn More >>
These ingredients are certified with:
Reference:
Cao, H., Gerhold, K., Mayers, J., Wiest, M., Watkins, S. and Hotamisligil, G. (2008). Identification of a Lipokine, a Lipid Hormone Linking Adipose Tissue to Systemic Metabolism. Cell, [online] 134(6), pp.933-944. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18805087.
Bernstein, A., Roizen, M. and Martinez, L. (2014). Purified palmitoleic acid for the reduction of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and serum lipids: A double-blinded, randomized, placebo controlled study. Journal of Clinical Lipidology, [online] 8(6), pp.612-617. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25499944.