Omega 7
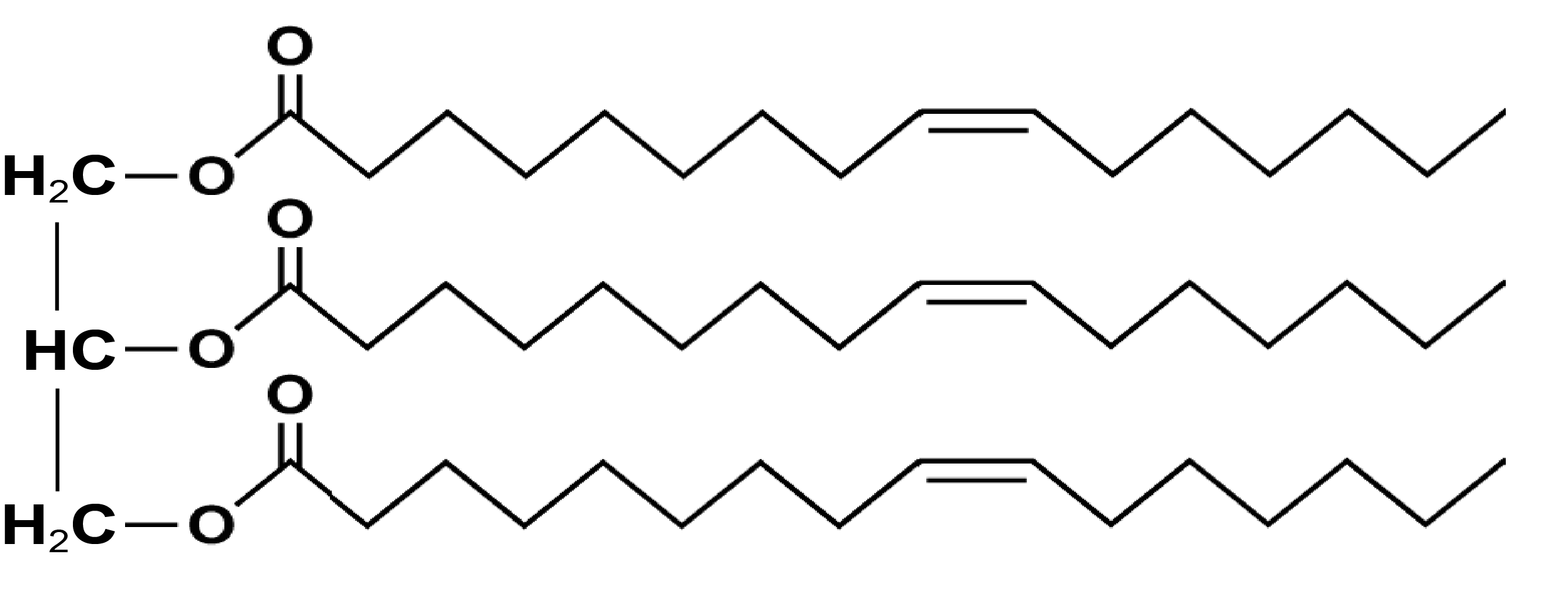
Chemical Structure of Omega 7
Omega 7 is a novel unsaturated fatty acid that was first discovered by scientists at Harvard Medical School in 2008. Researches have shown that Omega 7 may help prevent cardiovascular disease, cholesterol accumulation and lipid deposits in blood vessels, in addition to aiding to stimulate mucous membrane regeneration in the ocular, oral, respiratory, intestinal, vaginal and skin tissues.*
In nature, Omega 7 can be found Avocado, Peruvian Anchovy Fish, and Macadamia Nut. However, Tibetan Sea Buckthorn has the highest Omega 7 content.
With our advanced supercritical CO₂ fluid extraction and purification technology, we are capable of extracting 45% or more Omega 7 (CardiOmegia™) in its natural triglyceride form, which is up to 4.5X higher compared with other Omega 7 sources.